Mobile Theatre for Buddy Holly Musical in Hamburg, Germany
General information
-
Location address
Hamburg
-
Location country
Germany
-
Year of construction
1994
-
Name of the client/building owner
Buddy KG
-
Function of building
Theatres & cinemas
-
Degree of enclosure
Fully enclosed structure
-
Climatic zone
Temperate - cold winters and mild summers
Description
Design
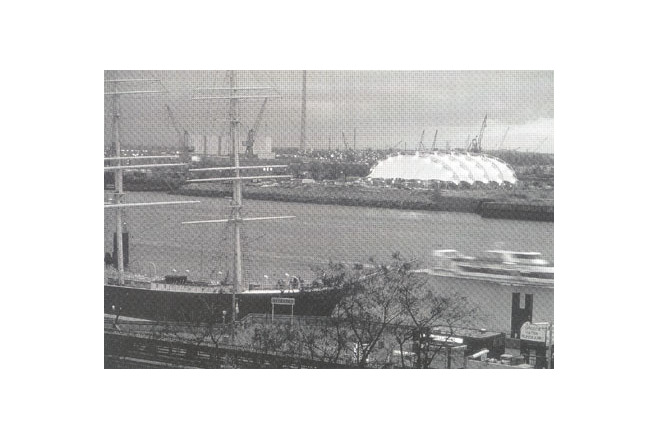
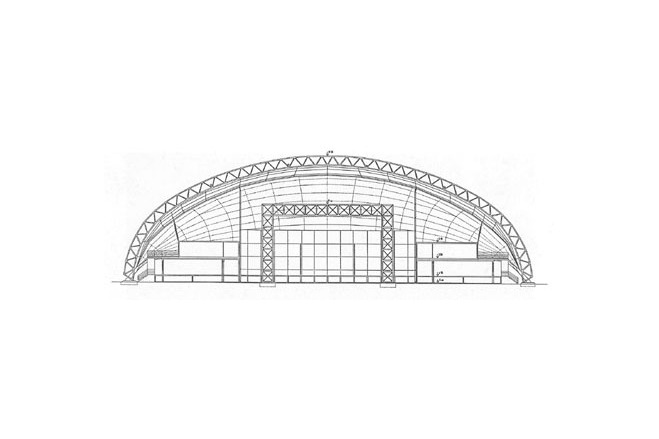
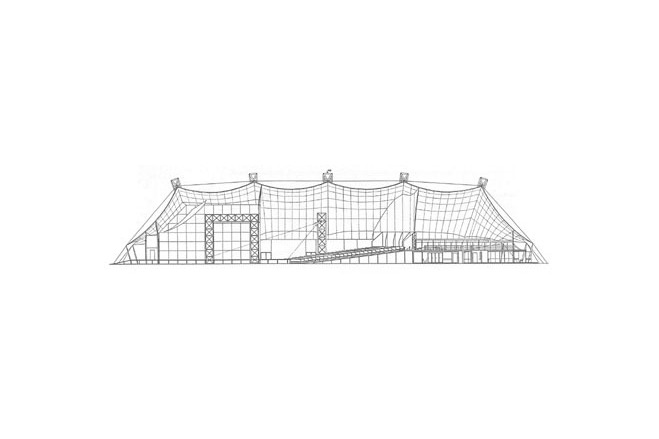
The 'Neue Metropol Theater' in Hamburg commissioned the construction of a mobile theatre which was to be used for the first time for a musical on the life-story of Buddy Holly, the Texan rock star who died in 1959 in a plane crash. The mobile theatre, with a textile roof structure covering a floor area of 500 m², was constructed in 1994 within the space of six months. The roof construction itself was designed and planned within only eight weeks. The theatre is located in the free port area opposite the St. Pauli pier.
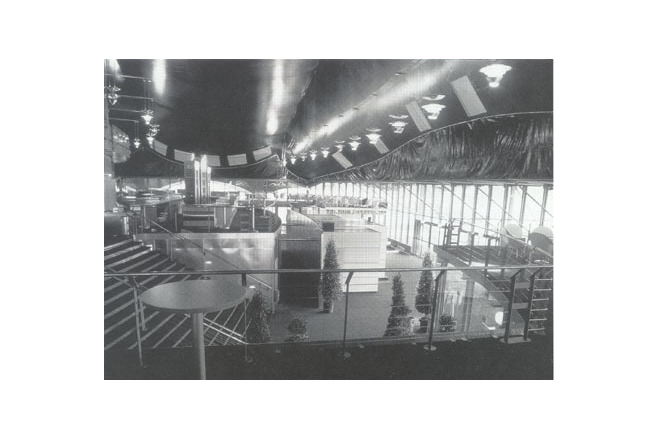
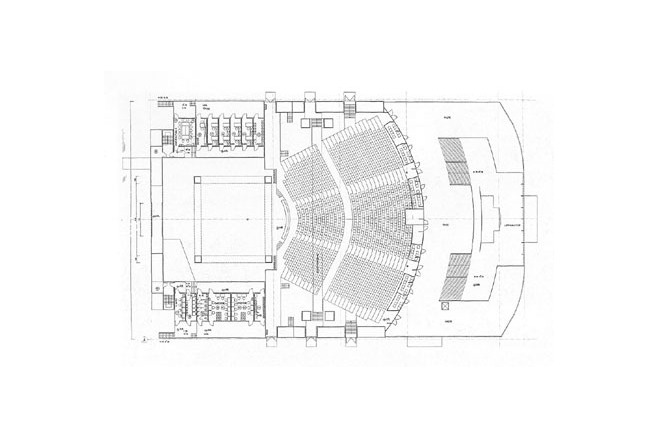
The membrane roof had to cover an auditorium with 1400 seats, with a main and two side stages as well as a two-storey lobby in the front part of the long, rectangular building.
The lobby was closed with a cable-stabilised glass façade, curved in plan, which offers a splendid view over the city and harbour.
The 1400 velvet-upholstered chairs are arranged under a dark blue ceiling; by skilfully arranging the 11 lower and 15 upper rows and the six boxes, no seat is further than 25 m away from the stage. Each row of seating is raised 12 cm above the one in front and thus offers a good view of the three stages.
The double-layer skin enveloping the building consists of an outer and an inner membrane, which serve simultaneously as weather protection, soundproofing and thermal insulation. The outer membrane is translucent, while the inner one is opaque, so that theatre performances are possible during the day. Although the structure is described as a mobile arched hall, it is conceived as a permanent building. After two years of service it is scheduled to be dissembled at the end of 1996 and set up again in a different location.
Structure
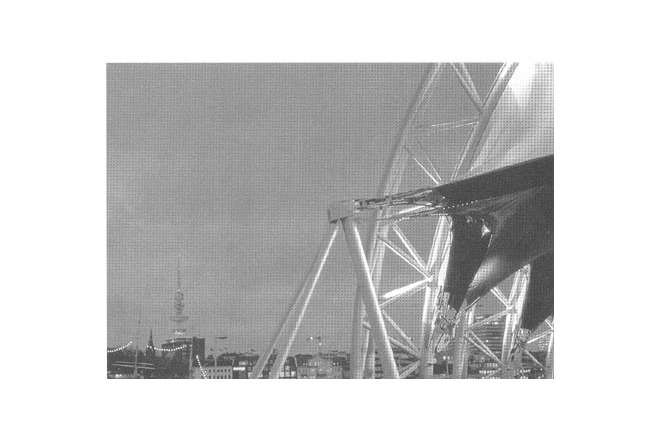
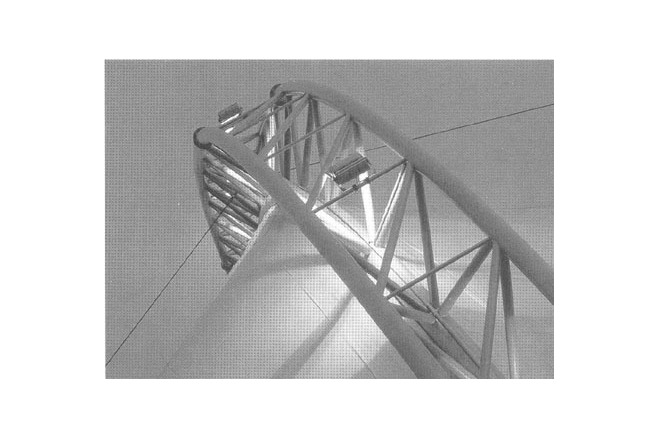
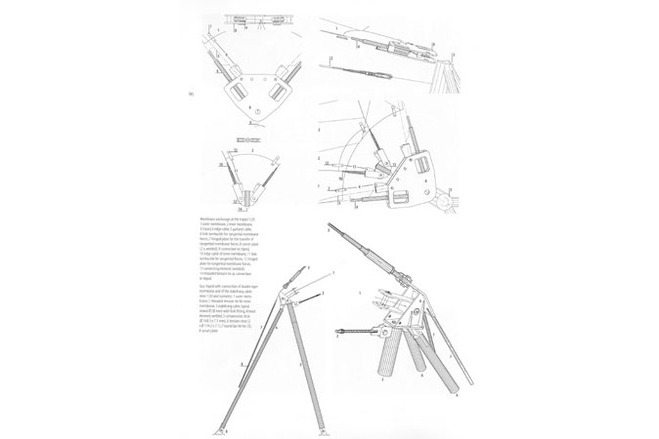
The primary structure consists of five welded pin-supported stell truss arches (at 15 m c/c), in the shape of a three-centre arch, with a span of 55 m and an effective depth of 1,5 m, which are stabilised in longitudinal direction through prestressed cables. The middle arches are vertical, the outer ones are slightly tipped to the outside which gives the building its distinct appearance. Each arch consists of five sections for ease of transport.
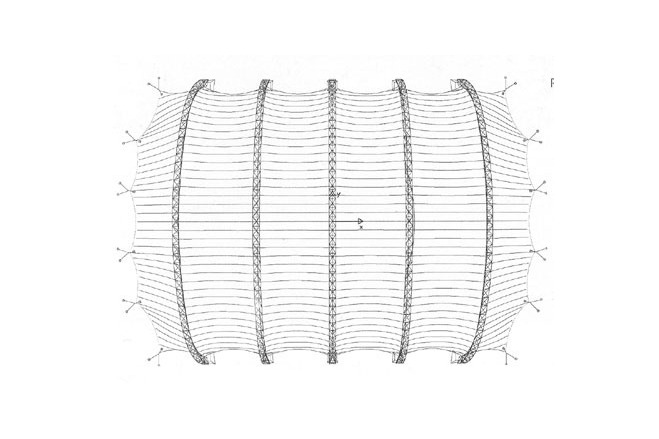
At each end of the building six tripods are placed, where both the stabilising cables and the edge cables of the roof membrane are attached. The building envelope consists of a double layer roof membrane of PVC-coated polyester fabric. The outside membrane is supported along the arches with a garland cable and intermittently connected to the arch bottom chord. The inner membrane is suspended in garlands under the arch. At the edge along the façade, both membranes are anchored via edge cables in arches and tripods and are prestressed from there.
Loads
For snow load 0,75 kN/m² were assumed, according to the German DIN standaard and to its location Hamburg. The design wind load is q = 0,8 kN/m² (v = 129 km/h) according to DIN standard.
Arches and tripods
The two-pin arches are braced in longitudinal direction by four prestressed cables, which join the arches; they are anchored at the building ends at the above-mentioned tripods. The self-supporting roof membrane spans between the arches. The three-chord tubular truss of mild steel St37 consists of five short, transportable sections, joined by high-strength friction grip bolts in a circular pipe flange: top chord tube Ø 244,5 x 8 mm, bottom chord Ø 323,9 x 16 mm, diagonals Ø 101,6 x 4,5 and Ø 114,3 x 7,1 mm, and the transverse struts in the middle arch Ø 48,3 x 5 mm.
A tripod consists of a compression member inclined at 15° to the vertical and of two diverging tension members with a steel bar tie fixed above to carry the forces from the stabilising cables.
Arches and tripods are protected by a zinc dust undercoat and by a double top coat; fittings and fixings are galvanised.
Membrane roof
The roof consists of four saddle-shaped membrane parts spanning between the five arches and of two free-form end membranes as transition from the arch form to the polygonal edge formed by edge cables.
For the existing brief this form has some distinct advantages:
Description of the environmental conditions
Heating, ventilation, air-conditioning
The spaces between the inner membrane and the upper edge of the façade as well as the internal membrane space along the roof edge are closed by a double layer sealing apron. A 40 to 80-cm thick airspace between inner and outer membrane provides thermal and acoustic seperation. A specially developed ventilation system allows effective and energy-saving air conditioning. Warm inner air is drawn into the membrane space, improved by adding fresh air and returned again into the auditorium. This method of circulating the air allows a multiple use of the already warmed inside air and thus leads to considerable energy savings. Seperately controllable exhaust fans in the apex of the hall complete the ventilation system.
In the summer the double membrane works as a cold roof. For natural ventilation of the membrane space both air inlets are available from the interior as well as from outside. The space is ventilated via roof vents in the upper part of the membrane.
[Soft Shells, Hans-Joachim Schock, p92-95]
Material of the cover
-
Cable-net/Fabric/Hybrid/Foil
Cable
-
Material Fabric/Foil
Polyester
-
Material coating
PVC
Main dimensions and form
-
Covered surface (m2)
500
-
Total length (m)
55
-
Total width (m)
95
-
Form single element
Anticlastic
Duration of use
-
Temporary or permanent structure
Permanent
-
Convertible or mobile
Convertible and mobile
-
Design lifespan in years
06-10
Involved companies
Editor
-
Editor
Marijke M. Mollaert