Morique Building
General information
-
Location address
Osaka
-
Location country
Japan
-
Year of construction
1992
-
Name of the client/building owner
Morique Building Co.
-
Function of building
Hybrid buildings
-
Climatic zone
Temperate - cold winters and mild summers
Description
Design
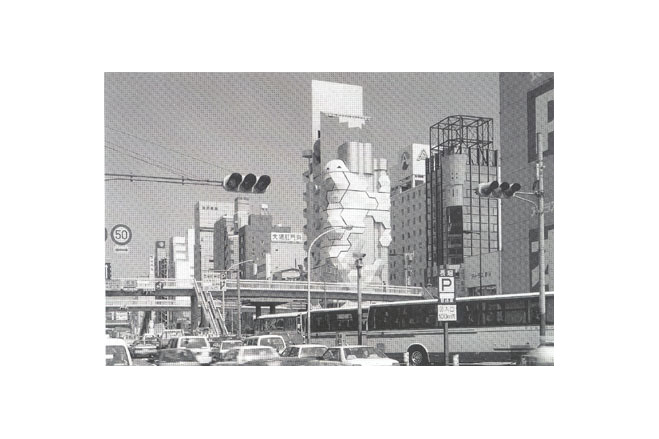
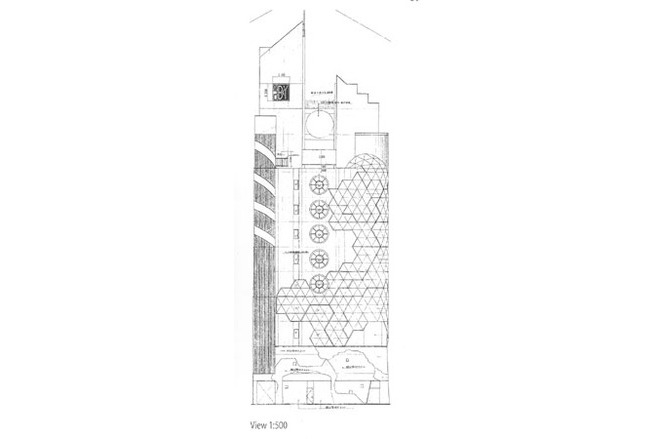
Clouds and water, symbollically represented as aluminium and fabric panels in a spatially curved curtain wall façade of a high-rise building: The Japanese architect Keizo Sataka wants to visually and formally create an expression of softness and tenderness, which contrasts with the angular shapes, hard materials and sharp edges of modern cities. Three-dimensional curved surfaces are intended to give the city a new, soft skin. As an expression of transition the architecture combines the standard aluminum façade panels of today with innovative panels of coated fabrics. Whether his architectural philosophy stands up to close scrutiny is one matter; the built architecture, however, is fresh and convincing.
Plan, use
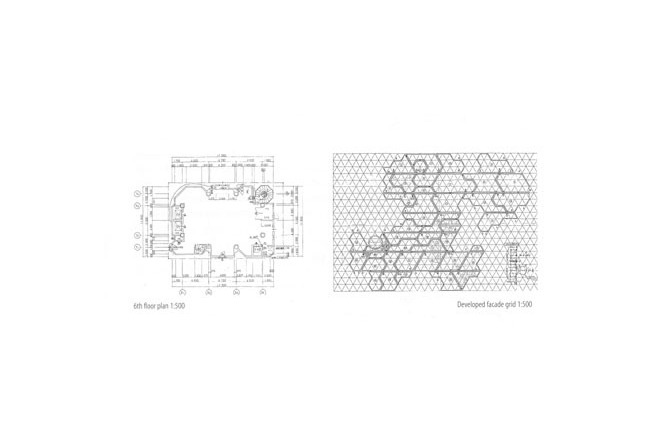
The building has a more or less rectangular plan with 9 storeys, 3 basements and a 4-storey penthouse. The leisure complex includes restaurants, bars, showrooms and a disco with a total floor area of 1978 m².
Structure
The high-rise structure consists of a three-storey reinforced concrete basement and composite steel and concrete decks in the upper floors. The design wind speed (typhoon load) is 60 m/sec (216 km/h). A wind tunnel test was not considered necessary.
Membrane panels and substructure
The aluminium and fabric panels are rain screen panels of a curtain wall façade in front of a space-enclosing and thermally insulating inner façade of polycarbonate panels. They are equipped with a bracing steel frame. All panels were prefabricated in the works, where the fabric membrane was prestressed against the steel frames. It is one of the first applications of coated fabric as a curtain wall façade. (Exhibition Hall 4 in Friedrichshafen), Germany is another, earlier example; it was erected around 1970). For Japan it is also the first building in which PTFE-coated glass fibre fabric (Shearfill II from Nitto Chemfab Co., Ltd.). As the façade was developed on a triangular grid the prefabricated panels consists of a changing number of grid triangles. They are braced by a welded steel frame (U 150 x 75 x 6,5/10 mm, CHS Ø 48,6 x 2,3 mm). At the edge the membrane is turned around the steel edge tubes of the frame and anchored in the steel U-section by clamping strip (FI 50 x 12 mm) and a welded on boltrope. At the clamps and turning points it is padded by neoprene strips, which also provide a wind and weather-tight seal. The panels are sealed and connected to each other by means of outer weather strips running up to a central cold rolled U - section (U 40 x 40 x 3 mm), where they are closed with a neoprene zipper gasket. The panel frames are welded to a hexagonal plate connecte via a steel plate (t = 12 mm) to the floor edge member (U 200 x 80 x 7,5/11 mm) and are thus anchored in the reinforced concrete floor behind (t = 150 mm).
[Soft Shells, Hans-Joachim Schock, p68,70]
Description of the environmental conditions
Material of the cover
-
Cable-net/Fabric/Hybrid/Foil
Cable
-
Material Fabric/Foil
Fiberglass
-
Material coating
PTFE
Main dimensions and form
Duration of use
-
Temporary or permanent structure
Temporary
-
Convertible or mobile
Convertible
-
Design lifespan in years
00-05
Involved companies
-
Architects
Keizo Sataka
-
Engineers
Taiyo Kogyo Corporation
-
Contractors
Taiyo Kogyo Corporation
Editor
-
Editor
Marijke M. Mollaert