Akita Skydome
General information
-
Location address
Kawabe-gun
-
Location country
Japan
-
Year of construction
1989
-
Name of the client/building owner
Akita Prefecture
-
Function of building
Sport
-
Degree of enclosure
Fully enclosed structure
-
Climatic zone
Temperate - cold winters and mild summers
-
Number of layers
mono-layer
Description
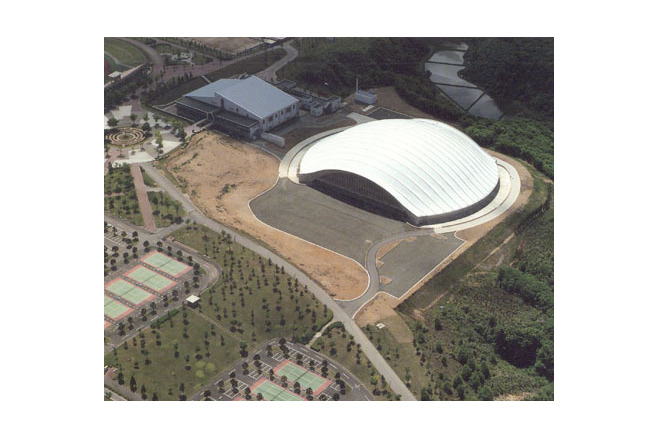
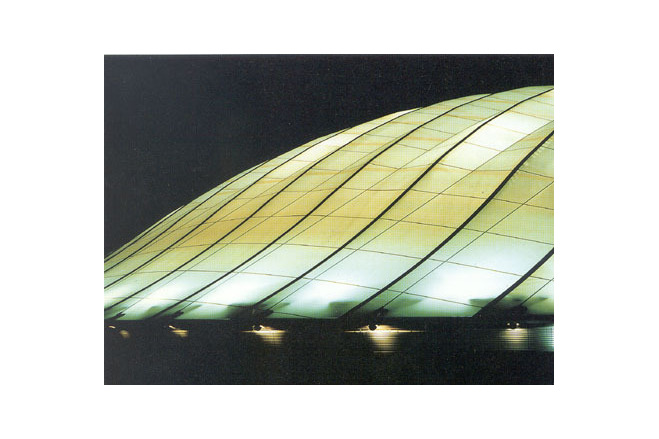
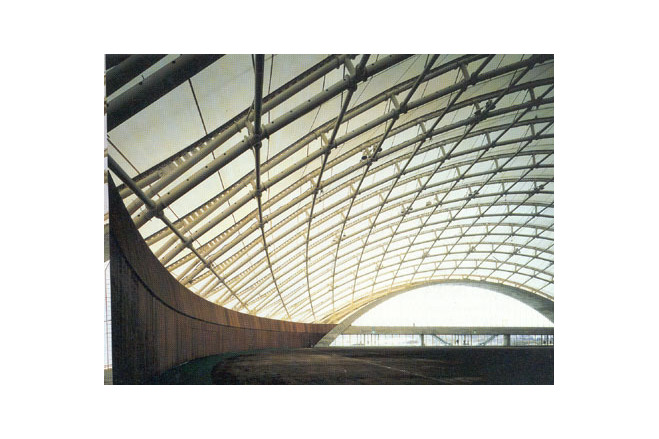
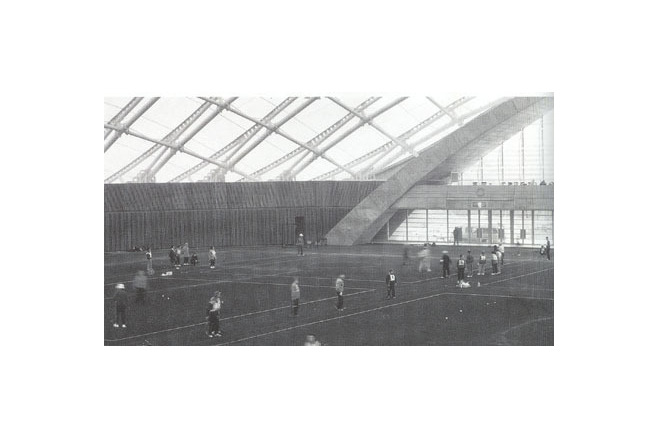
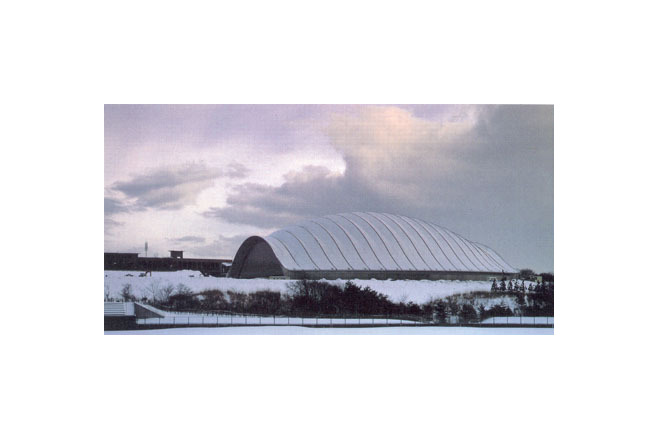
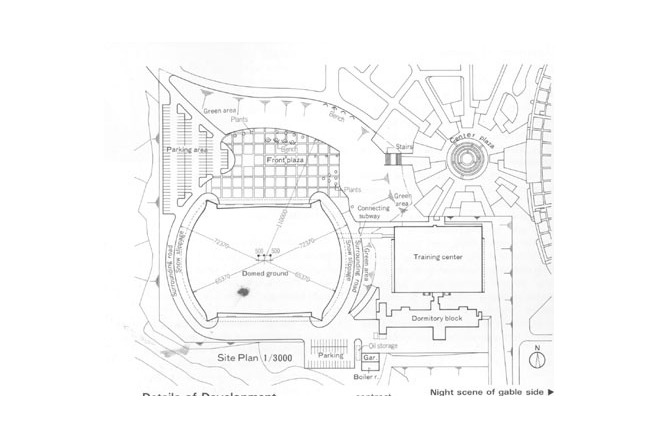
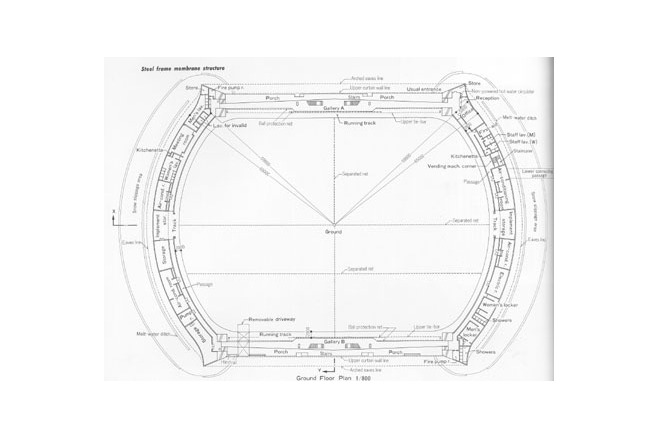
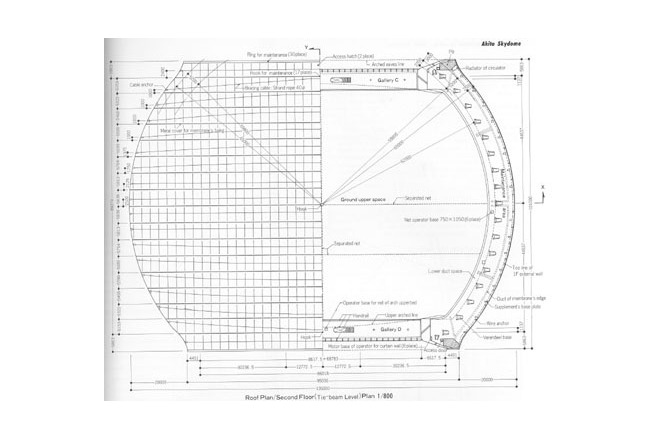
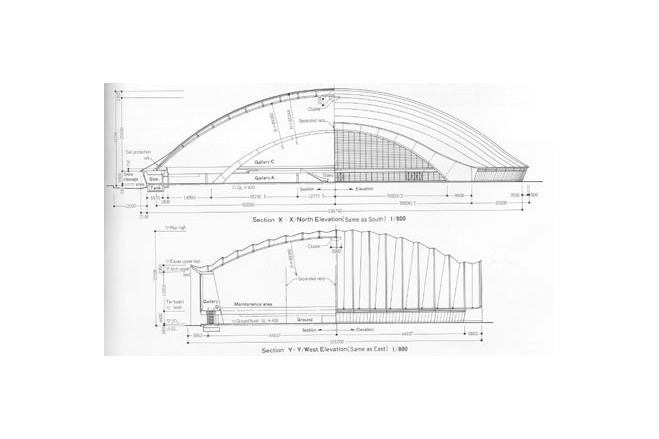
The program for the competition by Akita Prefecture basically had two objectives, " an athletic field with dry soil" and "a space with an outdoor feeling." It expressed the strong desire of the prefecture to promote the helth of its citizens and to improve the quality of life in winter. Translucency was considered vital to the creation of a sports space with an outdoor atmosphere. Consequently, a single-layered membrane structure was employed, and various measures to accelerate snow slippage were divised. The siting of the building in the direction of wind and snow in winter, the streamlined overall configuration and the membrane roof with smooth, one-directional troughs that are V-shaped in section are intended to reduce snowdrifts and the accumulation of snow and facilitate the slippage of snow. The entrance was situated on the gable side, where there is little snow-drift, and pond-like snow slippage areas of sufficient width were created in the directions in which snow would slip. Super space arches (three-dimensional arches made of steel pipes) capable of withstanding a snow load of 450 kgf/m were used for the framework. These arches are used as ducts for the warm air delivery system. Warm air is supplied evenly from numerous jets distributed over the entire roof. This system induces slippge with little energy and assures the safe shedding of snow at intended times. The ducts are also used to prevent the base of the arena from cooling, to prevent condensation and to remove heat in summer.
The design deals of course not just with snow. The gable ends can be opened completely to permit natural ventilation and to create a continuity with the outdoors. Akita Skydome combines diverse systems. The architectural deign and the system regulating the interior environment are integrated and create an entirely new living space.
(Masaru Ozaki, Kajima Design)
The site is in a region where over 150 cm of snow can accumulate but the structure was to have a lightweight, translucent membrane roof. Thus quite difficult, contrary conditions had to be met. A rational structural system able to support the snow load would not have sufficed. A configuration that prevented the accumulation of snow as much as possible and facilitated the slippage of any accumulated snow in a fixed direction was necessary.
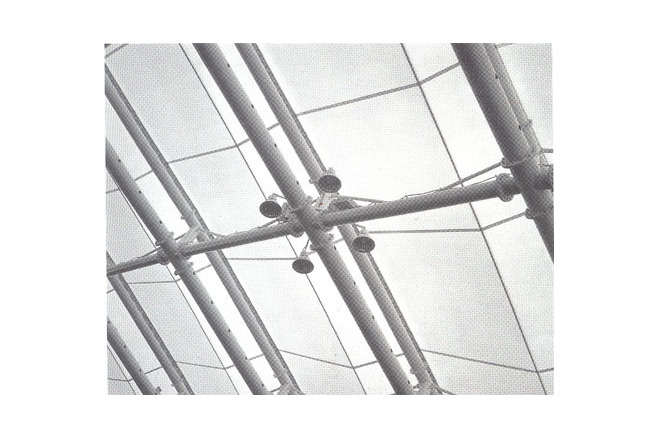
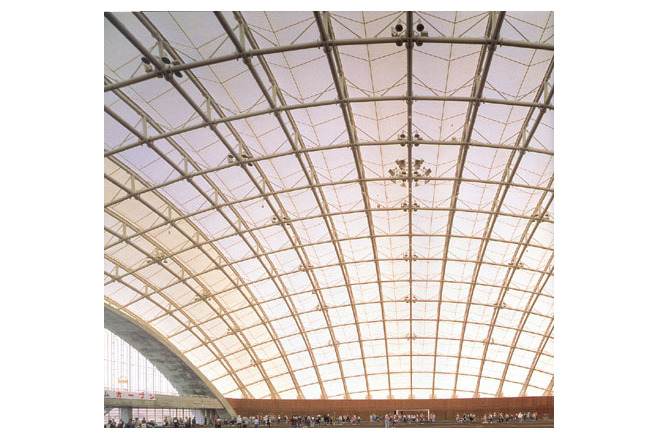
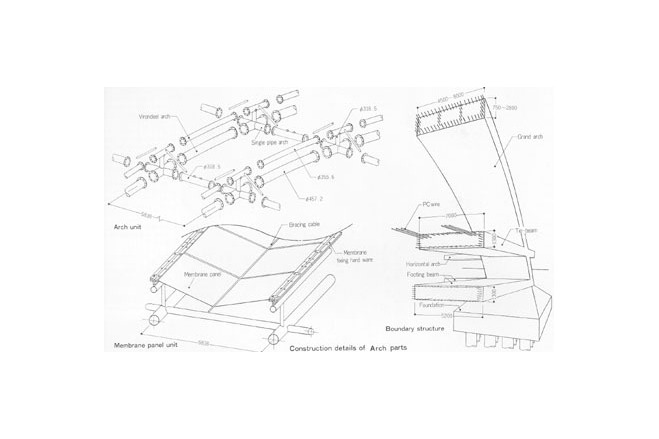
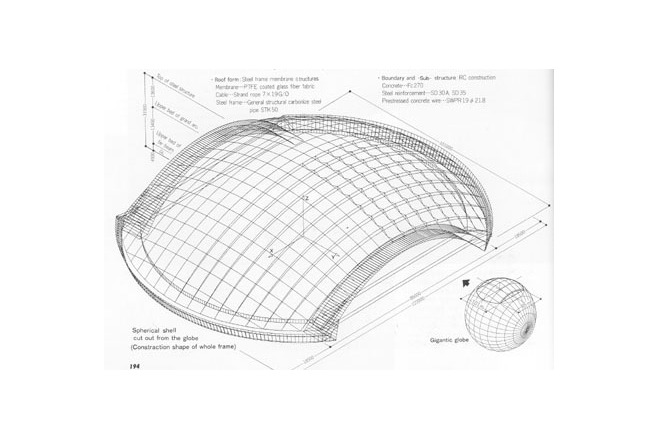
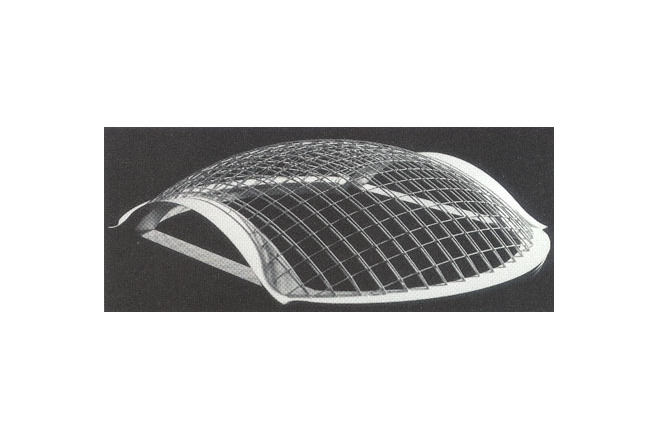
The framework supporting the membrane roof differs slightly from the configuration of the membrane. To arrive at a dynamically rational solution, the framework was made a simple figure cut out from a sphere. A geometrical grid is composed from intersecting arches. In the direction of the troughs. Vierendeel trusses are formed by connecting pairs of arches with struts, making the flow of forces an isotropic. Using steel pipes for the arch members and making the joints three-dimensionally rigide made it possible to create a three-dimensional grid of arches without any diagonal membeers and to avoid anything that might diminish the effect of lightness achieved by the membrane structure.
Construction began with the reinforced concrete boundary structure, which is practically all curved and in places changes curve three dimensionally. To deal with this, a form centering system developed in what was then West Germany was used.
The steel-pipe arch members were made into components. Divided into joints and simple arches, they were delivered to the site, assembled on the ground into large units, each representing one fifth of a pair of arches, and then erected while temporarlly resting on movable supports. The membrane was then attached, using a new membrane installation device that moved freely above the arches.
(Shigeru Ban, ex-member of Kajima Design)
[Membrane Designs and Structures in the World, Kazuo Ishii, p 244,246]
Description of the environmental conditions
Material of the cover
-
Cable-net/Fabric/Hybrid/Foil
Cable
-
Material Fabric/Foil
Fiberglass
-
Material coating
PTFE
Main dimensions and form
-
Covered surface (m2)
12200
-
Total length (m)
131
-
Total width (m)
101
-
Form single element
Anticlastic
Duration of use
-
Temporary or permanent structure
Temporary
-
Convertible or mobile
Convertible
-
Design lifespan in years
06-10
Involved companies
-
Architects
Kajima Design
-
Contractors
Editor
-
Editor
Marijke M. Mollaert