Rotunda, Compound Building
General information
-
Location address
Yokohama City, Kanagawa Pref.
-
Location country
Japan
-
Year of construction
1987
-
Name of the client/building owner
Misao Shigemoto
-
Function of building
Hybrid buildings
-
Climatic zone
Temperate - cold winters and mild summers
Description
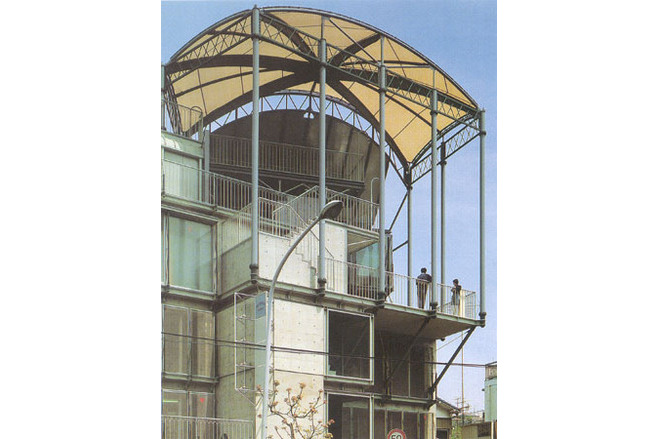
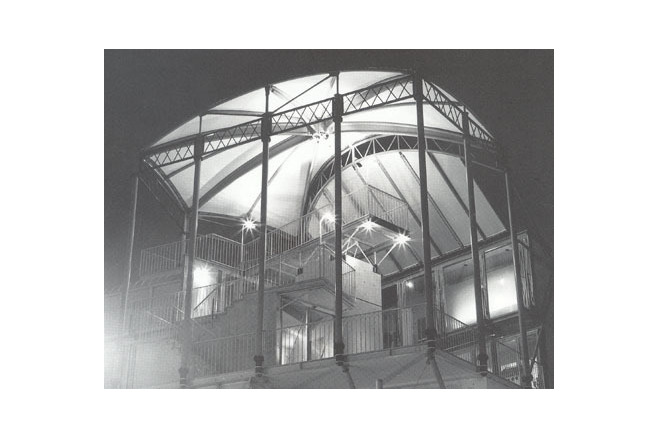
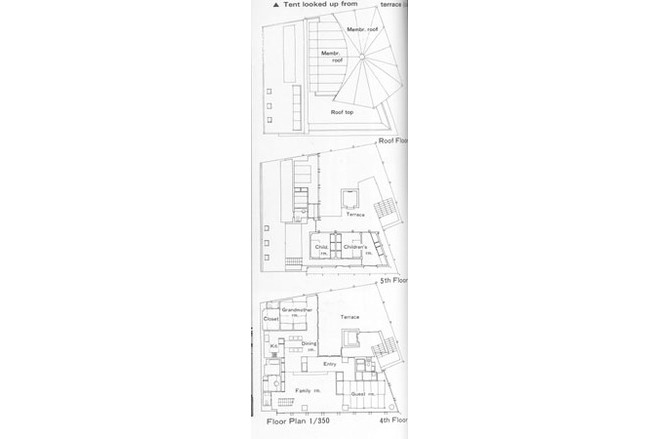
This building is almost identical to the <GAZEBO> except for small differences in size. It houses a garage and a store on the first floor, a rental office on the second , rental rooms on the third, and the owner's residence on fourth and fifth floors.
Similar to the <GAZEBO>, the exterior of second and third floors are covered by stainless steel mesh. During the day, it is almost impossible to see through from the outside into the interior. Through experimentation it was discovered that stainless steel mesh has a high degree of sound insulation than had previously been expected. All in all, it has proven to be a fairly suitable material for external walls of these types of combination buildings.
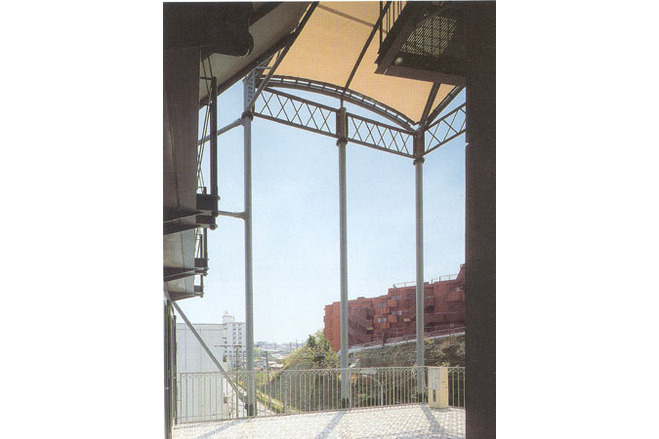
Another difference from the <AZEBO> is its position. It is located at inflected point in a road. From the viewpoint of a paaserby, it appears larger than actually is. The membrane roof has marked this building's image as outstanding amongst the varied types of architecture in this neighborhood's menagerie.
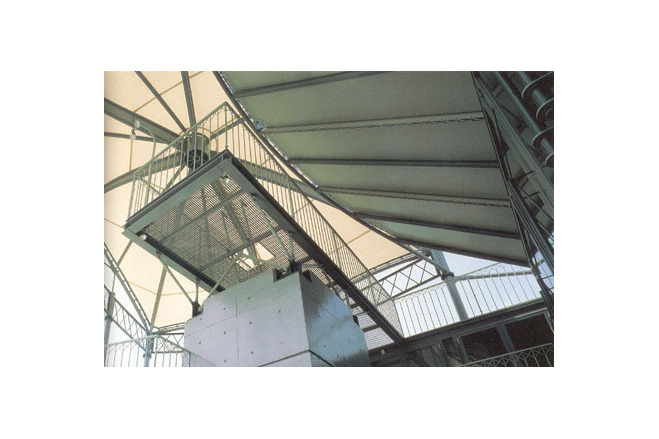
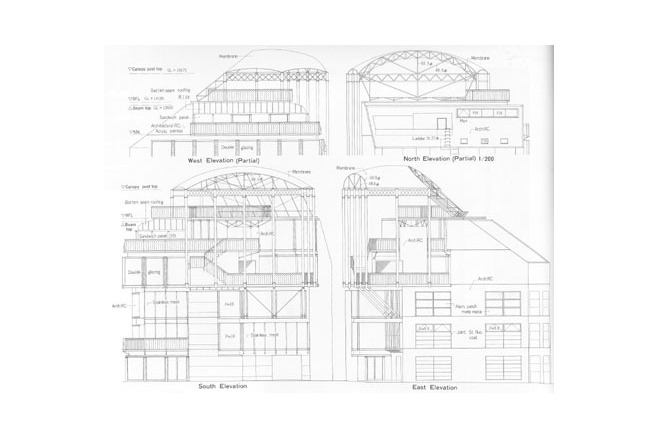
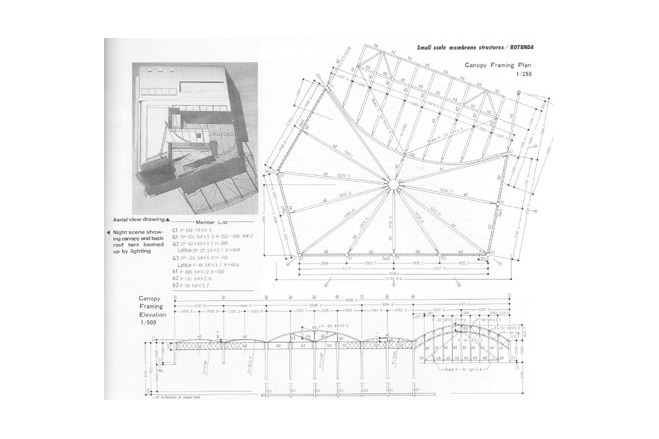
The tent-like covering used was framed by the same type of structure as was erected for <GAZEBO>. In this case, the only exception was the quality of the material. The uppermost floor covering is a semi-transparant PTFE coated glass fiber membrane. PTFE coated glass fiber membrane can withstand a state of high tension continually. In this way the membrane is also used as a structural member - it maintains the rigidity of the roof surface.
Generally, PTFE coated glass fiber membrane needs complicated fittings, such as Jaw-bolts , to introduce tensile force. This device is used to adjust and elongate the membrane. To make it simple, inverted U-shaped metal fittings, with several hooking holes were used. Through changing holes, elongation was able to be altered. The membrane material could thereby be adjusted to keep its rigidity.
[Membrane Structures in Japan, Kazuo Ishii, p 298, 299]
Description of the environmental conditions
Material of the cover
-
Cable-net/Fabric/Hybrid/Foil
Cable
-
Material Fabric/Foil
Fiberglass/polyester
-
Material coating
PTFE/PVC
Main dimensions and form
-
Covered surface (m2)
849
Duration of use
-
Temporary or permanent structure
Temporary
-
Convertible or mobile
Convertible
-
Design lifespan in years
00-05
Involved companies
-
Architects
Riken Yamamoto and Field Shop
-
Engineers
Kojima Structural Design Office
-
Contractors
Taiyo Kogyo Corporation
-
Suppliers
Taiyo Kogyo Corporation
Editor
-
Editor
Marijke M. Mollaert